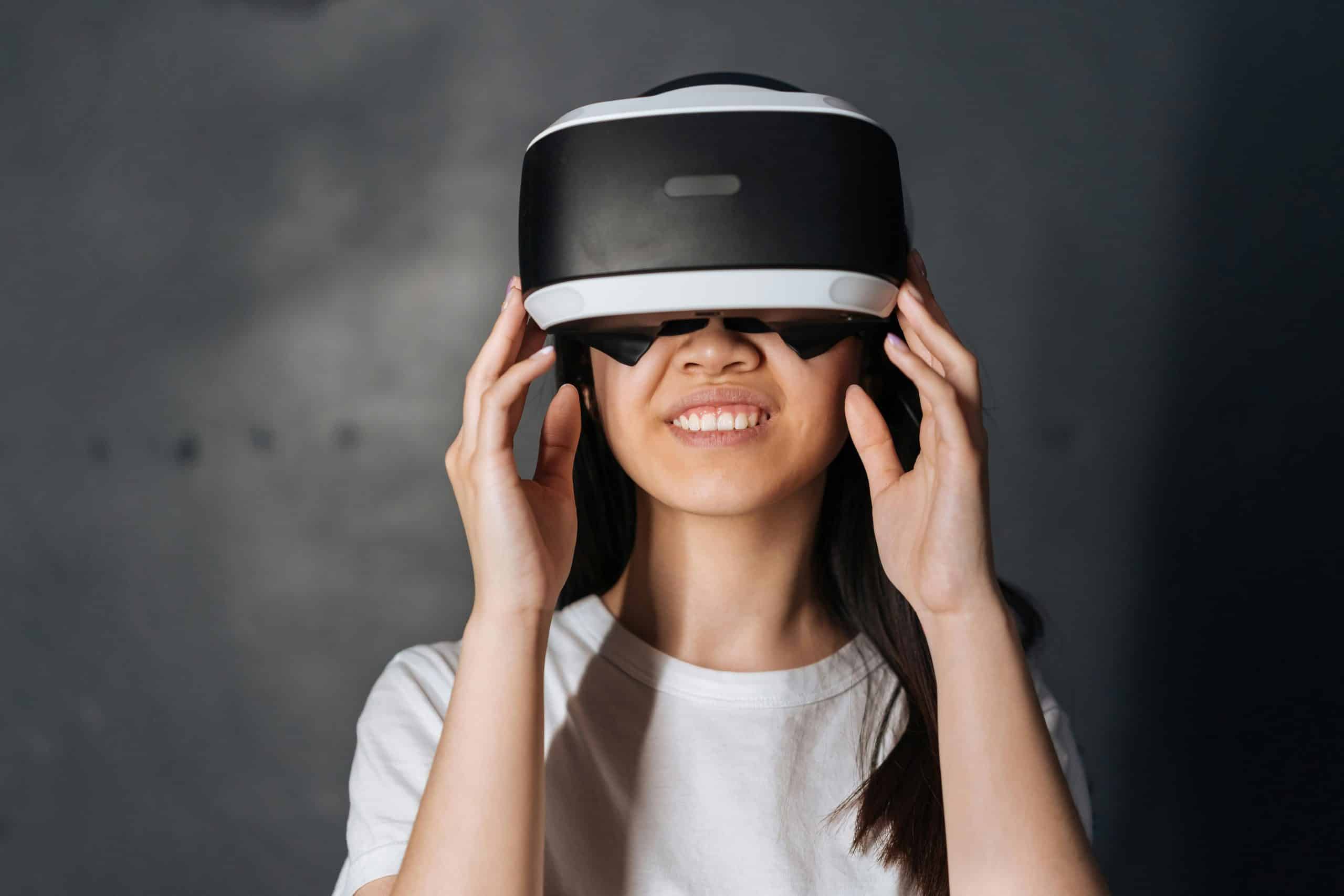
As technological innovation continues to shape our world, it has also begun to transform our understanding and engagement with our cultural heritage. At the forefront of this change is Augmented Reality (AR), a digital tool that allows us to superimpose virtual content onto the real world. In the context of cultural tourism, this technology advances the way we experience and learn about our past.
In cities across the UK, AR applications have been launched to liven up the historical narrative and present another layer to the overall experience. But how exactly are these applications contributing to an enriched cultural understanding and how can you use them for an in-depth historical tour? Let’s dive in to find out more.
Topic to read : Itineraries in Rome with the Turbopass: Exploring the Eternal City made easy" :
The Intersection of Augmented Reality and Cultural Heritage
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that merges the virtual world with the reality we live in. By overlaying digital information – in the form of text, images, audio or video – onto our view of the real world, AR enhances our perception and understanding of our surroundings.
When applied to the area of cultural heritage, AR can bring the past to life in a vivid and immersive way. It allows users to interact with historical figures, walk through ancient ruins, or explore a city as it looked centuries ago. This is not merely a game or an entertaining diversion – it’s a revolutionary way to convey historical and cultural knowledge.
In parallel : What Are the Advances in AI for Predictive Maintenance in UK Manufacturing?
How AR Works in Historical Tours?
AR applications for cultural heritage and tourism are generally location-based, meaning they use the GPS and compass in your mobile device to determine your position and orientation. When you point your device at a certain landmark, the application recognises it and overlays relevant historical information or digital reconstructions.
For instance, imagine standing in front of the Tower of London. With an AR application, you could visualise the execution of Anne Boleyn, hear the cries of the crowd, and see the architectural changes the tower has undergone over time. This multi-sensory experience is not possible with traditional tour guides or audio guides.
The Benefits of AR in Cultural Heritage Tourism
AR applications offer a new dimension to the cultural heritage experience. They allow the past to be seen, heard, and even lived, providing an immersive journey through time that enriches understanding and deepens engagement.
For cities with a rich historical past like London, Edinburgh, or Cardiff, AR has the potential to add a whole new layer of content and depth to the visitor experience. Not only does it make historical sites more interactive and engaging, but it also gives tourists the ability to explore the city at their own pace and according to their own interests.
Moreover, AR technology promotes accessibility in cultural heritage tourism. People who are unable to visit a site in person, for whatever reason, can now experience it virtually from anywhere in the world.
Utilising AR for Historical Tours in UK Cities
So, how can you utilise AR for your historical tours in UK cities? The first step is finding the right AR application. There are numerous apps available for iOS and Android devices, many of which are free or very affordable. These include popular choices like "HistoryView VR," "WWI A Tale of Two Trenches," and "Windsor Castle AR Tour."
Once you’ve downloaded an app, all you need is your smartphone or tablet. As you walk through the city, the app will guide you to points of interest and provide you with enriched historical content. Remember that you’ll need a strong data connection or pre-downloaded content for the AR experience to work smoothly.
Finally, don’t just rush from one site to another. Take your time to truly soak in the experience that AR offers. Listen to the stories, observe the digital reconstructions, interact with the virtual characters. Let the past come alive around you and unlock the rich cultural heritage that UK cities have to offer.
In summary, AR is not merely reshaping the way we perceive the world around us; it’s redefining how we engage with our past. It’s a powerful tool that can transform cultural heritage tourism into an immersive, interactive, and deeply engaging experience. As such, it’s an exciting time for both the tourism industry and history enthusiasts. As AR technology continues to evolve, we can only imagine the possibilities it will bring for cultural heritage exploration.
The Impact of AR on Tourism and Cultural Heritage Industry
With the advent of augmented reality, the tourism and cultural heritage industry are witnessing a paradigm shift in the way they operate and engage with visitors. This digital tool is not only enhancing the visitor experience but also revolutionising the way we perceive, understand, and interact with the past.
AR allows us to see more than meets the eye. When you point your mobile device at a historical site, the AR application recognises the location and provides you with virtual content that overlays your real-time view. This could include text, images, audio, or video that enrich your understanding of the site’s significance and history.
In essence, AR applications act as an interactive guide, taking you on an immersive journey through time. They bring to life the stories hidden in the bricks and stones of ancient monuments and historical sites, enabling you to see, hear, and even interact with the past. This is a marked improvement from traditional tour guides or audio guides, which could only provide one-dimensional information.
The impact of AR on the tourism and cultural heritage industry is far-reaching. It not only makes historical sites more interactive but also more accessible. For instance, someone who cannot visit the Tower of London in person can now witness its history unfold from the comfort of their home. AR applications have thus democratised access to cultural heritage, making it possible for anyone across the globe to virtually explore and experience historical sites in real time.
In addition, AR is a powerful tool to attract a new generation of tourists. The younger generation, who are digital natives, find this technology appealing and engaging. Therefore, integrating AR into the tourism industry keeps it relevant and appealing to a wider, tech-savvy audience.
Conclusion: The Future of AR in Cultural Heritage Tourism
The future of augmented reality in cultural heritage tourism looks promising. As this technology continues to evolve, it will unlock new possibilities and offer even more immersive and engaging experiences.
Imagine touring a city like London or Edinburgh with an AR application that not only provides you with historical facts but also enables you to interact in real time with virtual characters, reconstructs ancient ruins, and lets you explore the city as it looked centuries ago. The possibilities are endless!
Already, AR applications like "HistoryView VR," "WWI A Tale of Two Trenches," and "Windsor Castle AR Tour" are giving us a glimpse of what the future holds. These applications are enabling users to travel back in time and experience historical events as they unfolded.
Furthermore, AR is opening up new avenues for the preservation and dissemination of cultural heritage. It provides a platform where historical facts and stories can be shared in a dynamic and interactive way, fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation of our rich cultural past.
In summary, augmented reality is not just a technological innovation; it’s a cultural revolution. It’s transforming how we interact with our past, making history more immersive, accessible, and engaging. It’s indeed an exciting time for the tourism and cultural heritage industry as they embrace this digital tool to enhance visitor experience and promote cultural heritage exploration. The combination of AR and cultural heritage tourism has the potential to redefine how we engage with history, making it a more interactive, personalised, and immersive experience.